The Public Comment is now open through March 25, 2026 on the Draft 2027 CMS QRDA I Implementation Guide, Schematron, and Sample File for Hospital Quality Reporting
Top
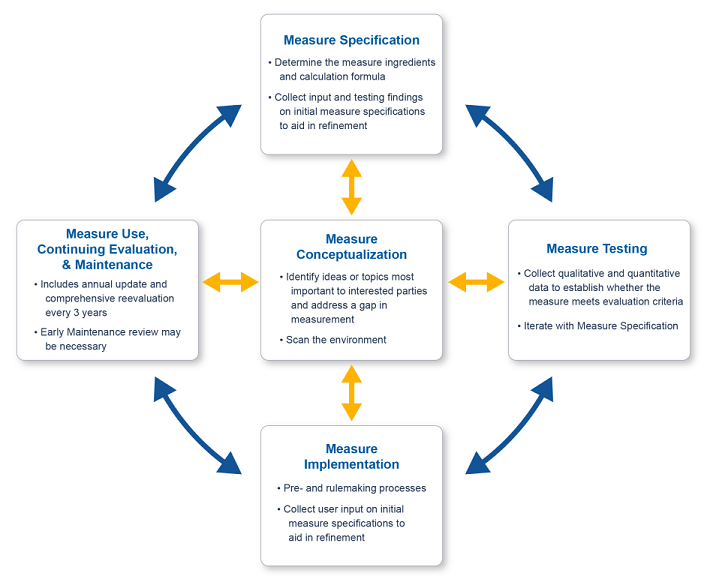
Electronic clinical quality measures (eCQMs) progress through multiple lifecycle stages.
- Measure Conceptualization
- Measure Specification
- Measure Testing
- Measure Implementation
- Measure Use, Continuing Evaluation, and Maintenance
The CMS Measures Management System Blueprint content outlines core processes for eCQM developers to follow when moving through the eCQM Lifecycle for the eCQMs used in various quality initiatives and programs.
Opportunities are available for the public to engage in the different stages of the eCQM Lifecycle including Call for Measures, Technical Expert Panels (TEPs), testing, and Public Comments.
There are five stages in the eCQM Lifecycle as shown in this graphic.
Conceptualization
Steps: Conceptualization initiates the eCQM Lifecycle. Perform an environmental scan to identify eCQM concepts, measurement gaps, determine the evidence base for eCQM concepts for development, look for competing and related measures, and draft the business case. The end goal of eCQM conceptualization is a meaningful, well-researched eCQM concept with well-defined initial components (e.g., initial population, denominator, numerator).
Tools and Resources: CMS.gov, CMS Measures Inventory Tool (CMIT), Environmental Scan Support Tool (ESST), focus groups, literature reviews, Measure Collaboration (MC) Workspace eCQM Concepts, ASTP/ONC Project Tracking System (Jira), Quality Data Model (QDM), stakeholder interviews, TEPs
Actors: Academics/researchers, CMS, eCQM developers, eCQM stewards, measured entities, patients/patient advocates/caregivers, public, researchers, subject matter experts (SMEs), TEP members
Specification
Steps: Electronic specifications for an eCQM are defined and developed iteratively so that eCQMs may be collected within certified electronic health information technology (IT) (CEHRT) systems and reported consistently, reliably, and effectively. Continue drafting the business case.
Tools and Resources: Binding Parameter Specification (BPS), Clinical Quality Language (CQL), CQL Evaluation Engine, CQL Execution Framework, CQL Runner, Cypress, eCQM Data Element Repository (DERep), Expression Logical Model (ELM), Health Quality Measure Format (HQMF), Measure Authoring Development Integrated Environment (MADiE), ASTP/ONC Project Tracking System (Jira), QDM, TEPs, Value Set Authority Center (VSAC), VSAC Collaboration Tool
Actors: eCQM developers, eCQM stewards, measured entities, patients/patient advocates/caregivers, SMEs, public, TEP members, tool owners
Testing
Steps: Iteratively test an eCQM's scientific acceptability (includes reliability and validity), feasibility, and usability and use. Test health IT’s ability to accurately calculate eCQMs. Continue drafting the business case.
Tools and Resources: BPS, Cypress, Health IT Certification for eCQM Reporting, Implementation Testing, MADiE, MC Workspace eCQM Testing Opportunities, ASTP/ONC Project Tracking System (Jira), Synthea™, TEPs, VSAC
Actors: Health IT vendors, eCQM developers, eCQM stewards, measured entities, patients/patient advocates/caregivers, public, SMEs, TEP members, tool owners
Implementation
Steps: eCQMs for many CMS quality programs must go through the rule-making process, CMS publishes adopted eCQMs for a given quality program in program rules (e.g., Physician Fee Schedule) and/or guidelines. Health IT vendors and measured entities implement eCQMs for a given quality program. Finalize the initial business case. Additionally, eCQMs may be submitted to the CMS consensus-based entity (CBE) for endorsement. eCQM developers are responsible for monitoring the CMS CBE’s eCQM requirements.
Tools and Resources: Certified health IT, CMIT, eCQI Resource Center, eCQM DERep, eCQM Implementation Checklist, Federal Register, ASTP/ONC Project Tracking System (Jira), TEPs, VSAC
Actors: CMS communication departments, health IT vendors, individual program technical assistance contractors, measured entities, patients/patient advocates/caregivers, public, SMEs, TEP members
Measure Use, Continuing Evaluation, and Maintenance
Steps: CMS receives stakeholder feedback on the implementation and use of eCQMs and shares with eCQM stewards and eCQM developers to improve future versions. If the eCQM is CMS CBE-endorsed, the eCQM must meet additional maintenance of endorsement requirements. eCQM developers perform an annual review and a comprehensive reevaluation every 3 years. CMS publishes updates to the eCQMs annually and may publish addenda to the updates. Compare actual performance with the initial business case.
Tools and Resources: CMIT, eCQI Resource Center, ESST, ASTP/ONC Project Tracking System (Jira), TEPs
Actors: Health IT developers, individual program technical assistance contractors, eCQM developers, eCQM stewards, measured entities, Network of Quality Improvement and Innovation Contractors, patients/patient advocates/caregivers, public, SMEs, TEP members
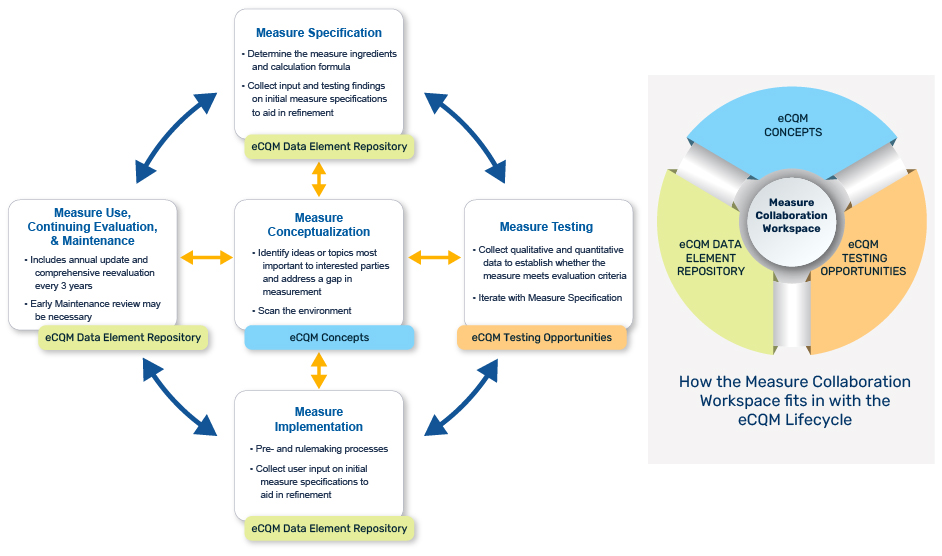
Use the Measure Collaboration Workspace to support the eCQM Lifecycle
This graphic highlights the key Measure Collaboration Workspace modules for use during various eCQM Lifecycle stages. Visit the Measure Collaboration Workspace, a set of interconnected resources, tools, and processes to promote transparency and better interaction across stakeholder communities that develop, implement, and report eCQMs.