The Public Comment is now open through March 25, 2026 on the Draft 2027 CMS QRDA I Implementation Guide, Schematron, and Sample File for Hospital Quality Reporting
Top
Clinical Decision Support (CDS) & Digital Clinical Quality Measures (dQMs)
Clinical Decision Support (CDS) targets improvement during care delivery, while electronic clinical quality measures (eCQMs) assess the quality of care after it has been rendered. Because they aim to enhance health care quality, their standards development is closely related. They share common data elements, terminology, technical specifications, and requirements.
Historically, CDS and eCQMs were developed using different standards—CDS often relied on proprietary or guideline-specific formats, while eCQMs used the Quality Data Model (QDM) for both data representation and logic. This divergence limited the reuse of machine-readable logic and created implementation burdens.
To address these challenges, CMS initiated a strategic shift toward digital Quality Measures (dQMs). This transition was catalyzed by broader efforts to modernize healthcare data interoperability, including mandates from the ONC 21st Century Cures Act requiring support for Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources® (FHIR).
In 2019, CMS replaced QDM logic with Clinical Quality Language (CQL). CMS is now transitioning eCQMs to dQMs using the FHIR-based standards. Not only does FHIR continue to support interoperability of data, it further enables standardized, electronic data sharing and expands data sources beyond traditional electronic health records (EHRs) to include other sources such as case management systems, laboratory systems, prescription drug monitoring programs, devices and patient-generated data. This shift reflects CMS’s strategy to modernize quality measurement.
Clinical Quality Framework (CQF) Initiative Harmonization
The Clinical Quality Framework (CQF) Initiative is an HL7 project led by the CDS and Clinical Quality Information work groups to identify, develop, and harmonize standards that promote integration and reuse of technical specifications between CDS and dQMs.
Harmonization of standards among CDS, and dQMs enhances the ease of implementation and supports scalable, interoperable health IT-enabled clinical quality improvement. Since the functions of CDS and dQMs are complementary, aligning their technical foundations enables more efficient development and deployment of quality improvement tools.
FHIR® and CQL - both HL7 standards - provide a common foundation for representing CDS and dQMs to
- suggest care to clinicians and care teams when there are opportunities to improve care quality
- assist with clinical workflow by gathering pertinent information before and during encounters for medication management, pre-certification, etc.
- measure if appropriate care was provided
The inclusion of dQMs further enables automated, scalable quality measurement using real-world data from FHIR-enabled systems, supporting continuous learning and improvement across health care settings.
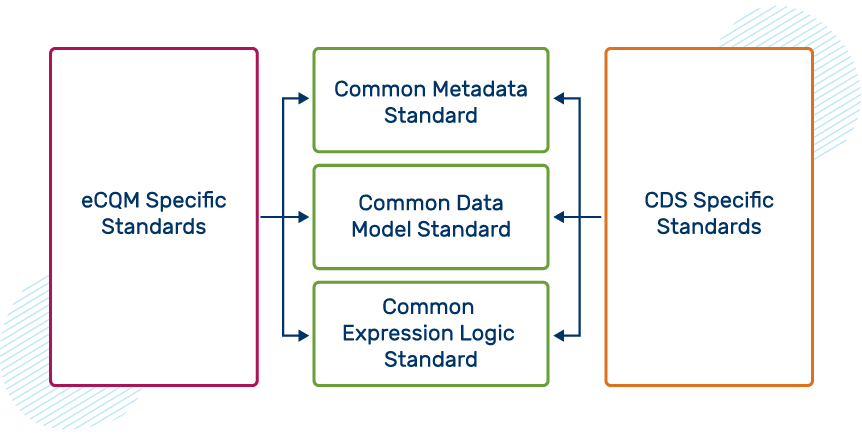
Common Shared Standards
The figure below shows eCQM-specific standards and CDS-specific standards coming together with common standards.
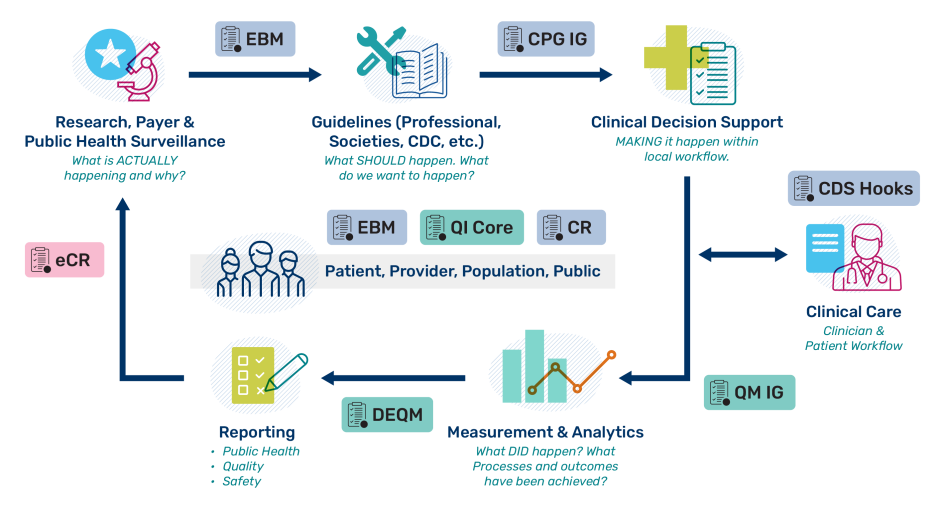
Current Shared Standards for Quality Management
The figure below (from FHIR Clinical Guidelines) depicts the Clinical Quality Lifecycle with situated standards to address each respective phase. The CPG-IG addresses a critical gap in explicitly formalizing the guideline recommendations and other guideline features as computer-interpretable for downstream consumption and closing the feedback and feedforward loop(s). Surveillance and feedback generates new evidence to update the guideline.
- EBM: Evidence Based Medicine on FHIR defines resources, terminology, and guidance for the representation of scientific knowledge, including support for citations, research study design, research results, assessments and aggregation of data, recommendations, and compositions of combinations of these types of knowledge.
- CPG: Clinical Practice Guidelines implementation guide supports the development of standards-based computable representations of the content of clinical care guidelines to support downstream capabilities such as cognitive and decision support, quality measures, case reporting, and documentation templates that direct clinical documentation in support of determining guideline compliance.
CDS Hooks: CDS Hooks version 2.0 specification for clinical decision support (CDS) outlines services to trigger clinical decision support, to prefetch required data, to analyze relevance to the clinical situation, provide recommendations and suggestions directly to system users (generally clinicians), capture reasons for overrides, and provide feedback to the CDS service.
- CQL: Clinical Quality Language is a high-level, domain-specific language focused on clinical quality and targeted at measure and decision support artifact authors. CQL is the expression language used to represent the logic that represents a measure, a CDS Hooks data request, measure report, practice guideline, case reporting, etc.
- QI-Core: Quality Improvement (QI) Core implementation guide defines a set of profiles that support creation of interoperable dQMs and CDS artifacts.
- eCR: Electronic Case Reporting implementation guide provides mechanisms for triggering requests to determine if patients presenting with new clinical conditions or findings require reporting to public health.
- QM IG: Quality Measure implementation guide provides criteria tailored for expressing quality measures including requirements for data retrieval and analysis.
- DEQM: Data Exchange for Quality Measures implementation guide addresses reporting data required for a set of quality measures.
Additional implementation guides include information about the management, use and development of FHIR artifacts. These two guides are:
- Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure (CRMI) implementation guide defines comprehensive guidance to facilitate the lifecycle management of FHIR knowledge artifacts such as value sets, profiles, libraries, rules, and measures used in multiple quality improvement and reporting domains.
- Using CQL with FHIR implementation guide provides guidance for using CQL to express data retrieval requirements and to analyze data received across use cases previously defined in domain-specific FHIR IGs (e.g., Quality Measures, Clinical Guidelines, etc.).