The Public Comment Period for Draft CMS FHIR® Digital Quality Measures (dQMs) is now open. Comment on Eligible Clinician dQMs, Hospital - Inpatient dQMs, and Hospital - Outpatient dQMs until February 23, 2026.
Top
Resources Subnav
FHIR is a Health Level Seven International® (HL7®) standard for exchanging health care information electronically. The health care community is adopting this next generation exchange framework to advance interoperability. Electronic health records (EHRs) represent patient data in different ways (e.g., medications, encounters) and FHIR provides a means for representing and sharing information among clinicians and organizations in a standard way regardless of the ways local EHRs represent or store the data. FHIR combines the best features of previous standards into a common specification, while being flexible enough to meet the needs of a wide variety of use cases within the health care ecosystem. FHIR focuses on implementation and uses the latest web technologies to aid rapid adoption.
FHIR includes a set of modules that group related resources, including the Clinical Reasoning Module, which supports the representation, sharing, and evaluation of clinical knowledge artifacts. The Clinical Reasoning Module covers resources for decision support rules, quality measures, order sets, clinical protocols, evidence summaries, and other computable clinical logic. It enables both real-time clinical decision support during care delivery and retrospective quality measurement using the same underlying artifacts and data structures, reducing duplication and improving consistency compared to earlier standards.
FHIR Quality Measurement
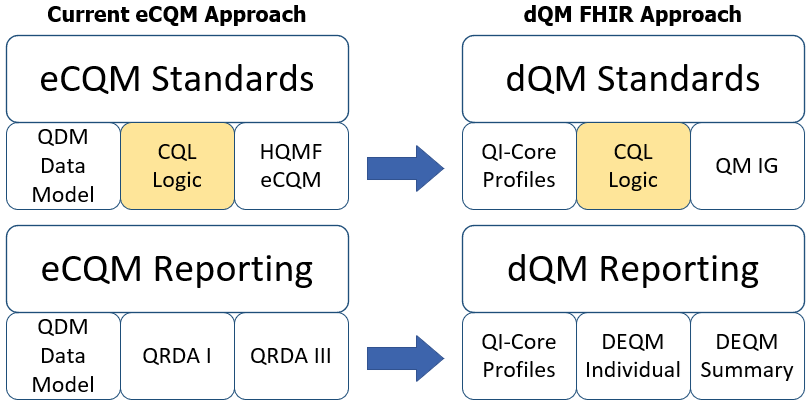
The health care community and CMS are transitioning to digital quality measures (dQMs). Today’s eCQMs continue to rely on established standards- including Quality Data Model (QDM), Clinical Quality Language (CQL), Health Quality Measure Format (HQMF), and Quality Reporting Document Architecture (QRDA), which remain the foundation for measure specification and reporting across MS quality programs.
FHIR introduces the potential for a more streamlined and interoperable approach. Because FHIR natively aligns with how EHR's exchange data in routine clinical workflows, it offers an opportunity to improve data availability for measurement, enhance alignment between quality measurement and clinical decision support (CDS), and reduce burden on measure developers, implementers and providers. As CMS and industry partners continue evaluation activities, FHIR-based quality measurement may enable more efficient, scalable, and clinically integrated approaches to measuring and improving care.
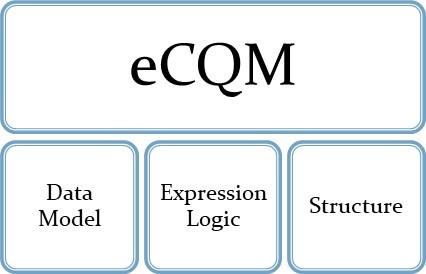
To effectively evaluate the transition to FHIR-based quality measurement, it is essential to understand the key components of an eCQM and how each component is expected to evolve with FHIR adoption. As illustrated in the graphic, an eCQM consists of three primary parts, the data model, expression logic, and structure.
- Data Model: Defines how the patient’s clinical data is represented and accessed to support measure calculation.
- Expression Logic: Specifies how the measures’ numerators, denominators, exclusions and exceptions are calculated and how performance is evaluated.
- Structure: Serves as the framework that organizes the measure’s metadata, logic, and population criteria.
The graphic below compares the current eCQM approach with the future dQM approach.
A FHIR eCQM uses the FHIR Quality Measure Implementation Guide and the Quality Improvement Core Framework (QI-Core) Implementation Guide. The goal is to align quality measurement standards for eCQM development and reporting:
- Standards used for dQMs have been developed to represent previous generations of standards used for eCQM development and reporting using FHIR. These implementation guides are the basis for dQM development and reporting: Quality Improvement Core (QI-Core) replaces QDM for clinical data. QI-Core is a version-specific data model built directly on top of FHIR resources (US Core and base FHIR resources).
- FHIR Quality Measure replaces HQMF for eCQM structure. The Quality Measure IG provides guidance in using the FHIR Measure resource for eCQM structure.
- DEQM individual and summary reporting replace QRDA I and QRDA III reporting.
Benefits of FHIR
- Real-time data access
Provides faster, real-time access to quality data
- Reduces burden for reporting quality measures
- Aligns CMS eCQM reporting with industry clinical data exchange framework, reducing implementation burden
- Enables automated data retrieval from EHRs and submissions of quality data through use of standards-based APIs
- Promotes interoperability
- Aligns data exchange requirements for quality measurement and reporting with interoperability standards used in other health care exchange methods
- Allows for additional quality data exchange methods
- Reduces effort to implement new measures
Simplifies data mapping to a single FHIR mapping vs. mapping to HQMF and QRDA
- Improves alignment between eCQMs and clinical decision support
Both use a common FHIR data model (FHIR QI-Core)
FHIR Resources
Resources are the basis for all exchangeable FHIR content. Each resource includes a standard definition and human-readable descriptions about how to use the resource. Each resource also has a set of common and resource-specific metadata (attributes) to allow its use clearly and unambiguously. FHIR Resources represent defined healthcare information - clinical, administrative and operational workflows which are the foundation for the data model used in quality measurement.
FHIR Profiles and Implementation Guides for Quality Measurement
A FHIR profile applies constraints and/or extensions to the base FHIR resource to support the requirements of a specific use case. Profiling does not change the underlying resource.
For example, a quality measure may need to capture a patient’s blood pressure using the FHIR Observation resource. In this case, the QI-Core Observation profile is used, which in turn relies on the US Core Blood Pressure profile. That US Core profile requires fixed LOINC codes and specific component codes for systolic and diastolic values. These constraints ensure that dQMs represent blood pressure consistently. When EHRs and downstream systems use the same profile, the exchanged data becomes more predictable, computable and reusable- including quality measurement.
The FHIR community often assembles multiple easily consumable profiles into implementation guides (IGs). As an example, QI-Core is an IG containing profiles for representing data used for dQM evaluation.
For the purposes of transitioning to dQMs, CMS is collaborating with HL7 to advance emerging standards and develop additional FHIR profiles for both dQM development and reporting.
| Data Model | Quality Measures | Measure Reporting | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Resource | US Core* | Measure Resource | Measure Report |
| Implementation Guide | QI-Core | FHIR Quality Measure Implementation Guide | DEQM |
*US Core is an implementation guide representing FHIR for the US Realm
Exchange Specifications
The FHIR exchange specification defines how systems exchange and manage resources across different environments. They describe several interaction patterns, including real-time Representational State Transfer (RESTful) application programming interfaces (APIs), messaging and document-based exchange.
RESTful APIs use the standard HTTP operations to create, read, update and search FHIR resources, enabling real-time, interoperable data exchange between systems. Messaging and document exchange support workflows that require asynchronous or bundled data communication.
These exchange specifications form the technical foundation for dQM reporting ensuring that measure data can be shared and evaluated consistently, reliably, and in a standardized format.
Disclaimer
FHIR® is the registered trademark of HL7 and is used with the permission of HL7. Use of the FHIR trademark does not constitute endorsement of the contents of this repository by HL7, nor affirmation this data is conformant to the various applicable standards.