The 2027 Annual Update draft measure specifications are now available. Question and comment on Eligible Clinician eCQMs, Hospital - Inpatient eCQMs, and Hospital - Outpatient eCQM until December 19, 2025.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is working to improve the health of our nation by transforming care from a volume-based, provider-centered system to a value-based, patient-centered system. This transformation uses quality measurement to improve care by measuring how patients are treated and, most importantly, how well those patients do afterward. eCQI activities provide common standards and shared technologies to monitor and analyze the quality of health care provided to patients and patient outcomes.

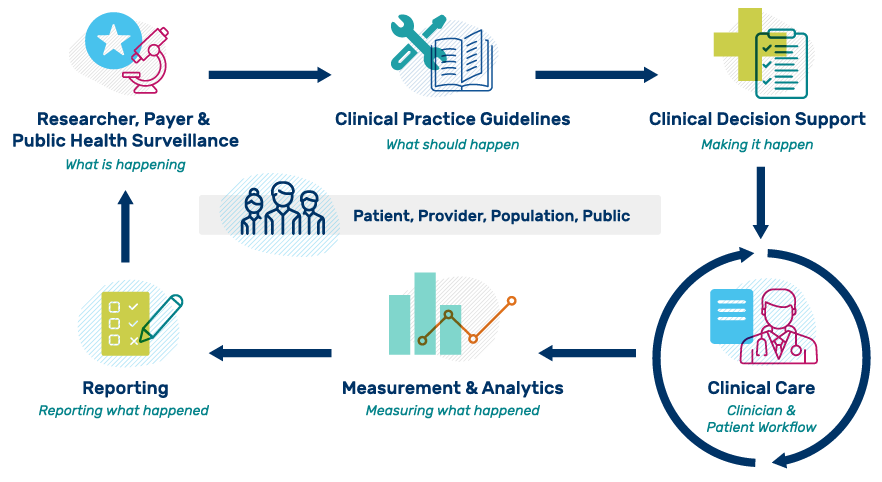
This eCQI Ecosystem graphic is adapted from an Health Level Seven International® (HL7) Clinical Quality Improvement workgroup graphic. The image highlights the ideal flow of evidence-based information to evaluate clinical performance and outcomes for health care organizations. Please note that while it is depicted in an orderly fashion, the process is often iterative between interested parties and phases.
Electronic clinical quality measures (eCQMs) measure the quality of health care provided by hospitals, clinicians, and other measured entities. The “e” in eCQM means performance is measured using data extracted from an electronic health record and/or health information technology (IT) system. eCQMs include data elements, terminology, logic, and definitions using HL7 standards, which represent a clinical quality measure in an electronic document that can be captured, stored, shared, and read electronically.
Advancements in the interoperability of health care data provide new opportunities to modernize CMS’s quality measurement systems. HL7's Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources® (FHIR®) Release 4 and specific data standards allow for the consistent representation and sharing among clinicians, organizations, and patients. The health care community and CMS are exploring a potential transition to FHIR-based quality measurement beginning with FHIR-based eCQMs.
Currently, most eCQMs primarily look back at recent activities to determine whether the measured entity adhered to the evidence-based standard of care for each patient. The next stage of quality improvement for health care transformation consists of using clinical decision support (CDS), eCQMs, and digital quality measures (dQMs) together. Rather than limiting quality improvement to retrospective measurement, we are moving to provide standards to express CDS that use evidence-based medicine and the patient’s own history, preferences, and data to customize care recommendations and actions for each individual patient.
CMS supports this transformation by aligning measure components, tools, and standards. Standards are essential to ensure data consistency, validity, and interoperability to better share information, develop software, integrate data, and implement systems. This alignment of standards is expanding the capability of electronic measurement beyond eCQMs to include dQMs, which incorporate a variety of data sources, such as case management systems, laboratory systems, and prescription drug monitoring programs. The use of data from multiple sources will enable more precise and usable information for measurement, population health surveillance, care coordination, and provide clinicians a more holistic view of every patient’s health with actionable data available at critical decision points. CMS invites you to view the Digital Quality Measures pages for an outline of activities to transition to digital quality measurement and to join the Quality Data Implementation User Group if you are interested in the standards to be used for this transition.